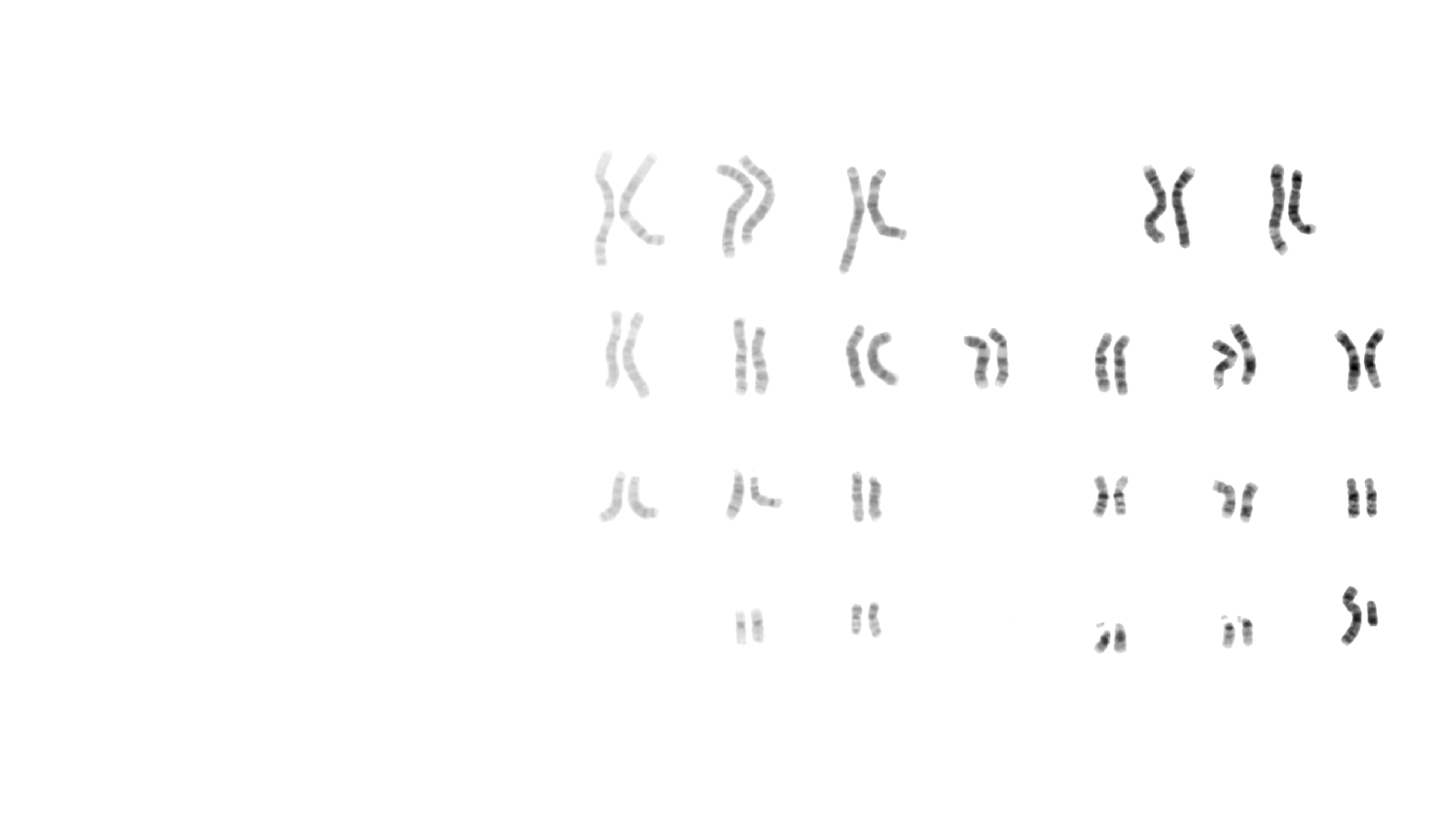
Cytogenetics
Definition
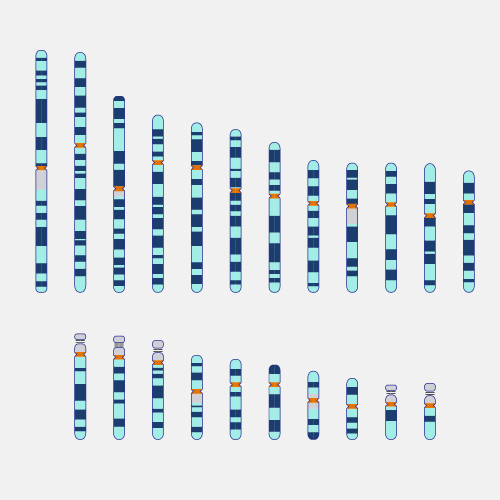
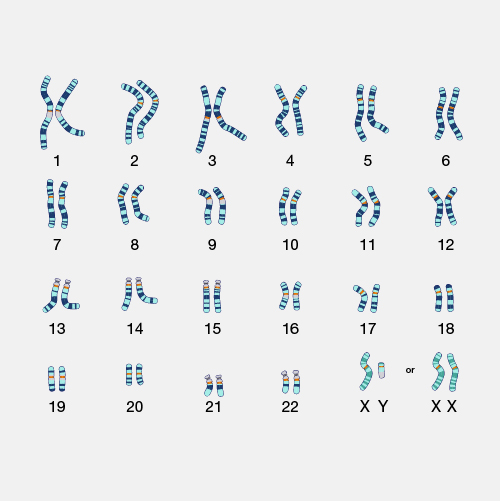
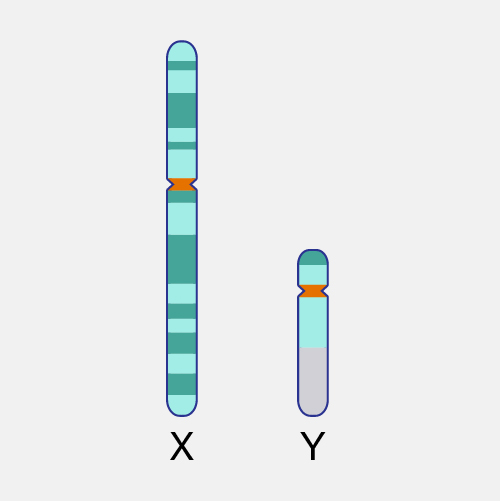
Cytogenetics is a branch of biology focused on the study of chromosomes and their inheritance, especially as applied to medical genetics. Chromosomes are microscopic structures containing DNA that reside within the nucleus of a cell. During cell division, these structures become condensed and are visible with a microscope. Special staining techniques can be used to assess the number and structure of a person’s chromosomes as part of diagnostic testing. The number and/or structure of chromosomes is known to be altered in certain genetic diseases.

Narration
Cytogenetics. Cytogenetics is the study of chromosomes in any species. Chromosomes are structures of DNA strands and protein that contain most of the genetic information in a cell. We can visualize chromosomes in metaphase during the cell cycle. Cytogenetics refers to the study of tissue, blood, blood marrow, or culture cells in a laboratory, using banding or manipulating techniques to look for changes in the chromosomes, including broken, missing, rearranged, or extra chromosomes. Changes in the chromosomes may be a sign of a genetic disease or condition. Cytogenetics may be used to help diagnose, plan a treatment, or find out how well a treatment is working.