Genetic Architecture
Definition
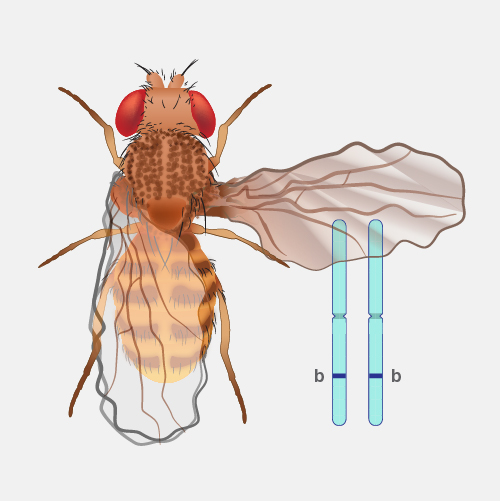
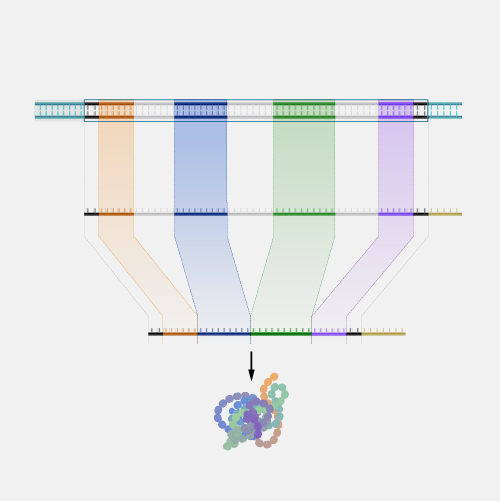
Genetic architecture describes the combined contribution of all genetic influences on the trait. This includes how many genes are involved, how common different versions or variants of those genes are in a population, what the individual effect of each variant is on the trade as well as how those variants act together. Mapping out the genetic architecture of a trait can help us understand its evolution and underlying biology. For traits that are related to a disease, knowing the genetic architecture may help us identify people at risk or find treatments.
Narration
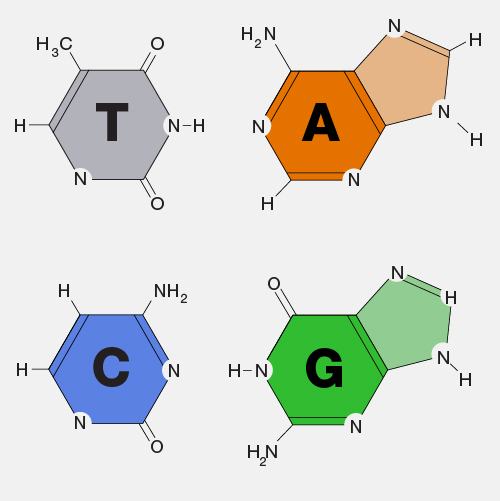
There are different ways we can think about how genetic differences among individuals influence traits or, in other words, the observable characteristics of a person or organism. One way to define genetic architecture is to find the number of gene differences, how common those are in a population, and how they all come together to influence differences in traits among individuals. Another way is to work out all the things that happen, such as the expression of genes in our cells or the development of the body, that connect the sets of genes found in an organism and the traits it has. Genetic architecture can thus refer to all parts in this map that describe how you get from genes to traits. In either case, because the effects of genes unfold in a given environment, the exact genetic architecture of a trait may depend on where, or when, or the context in which organisms are living.