Point Mutation
Definition
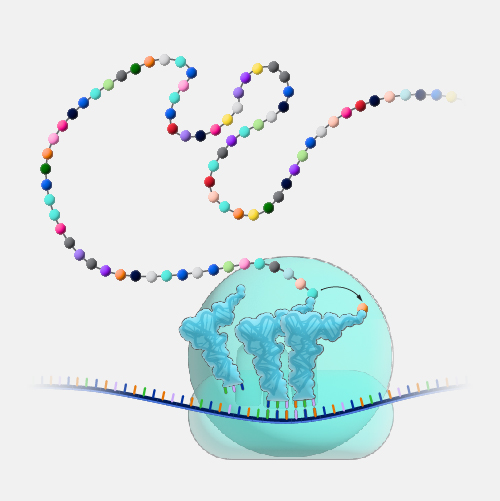
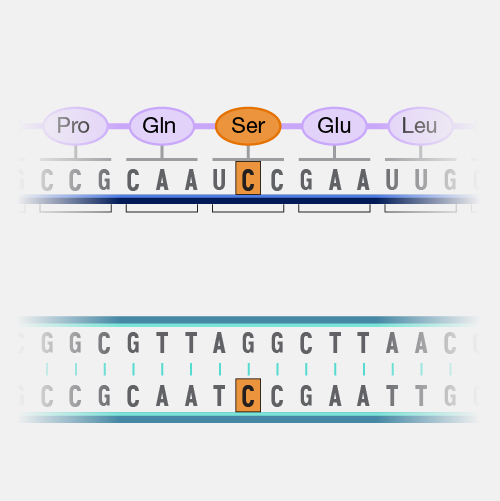
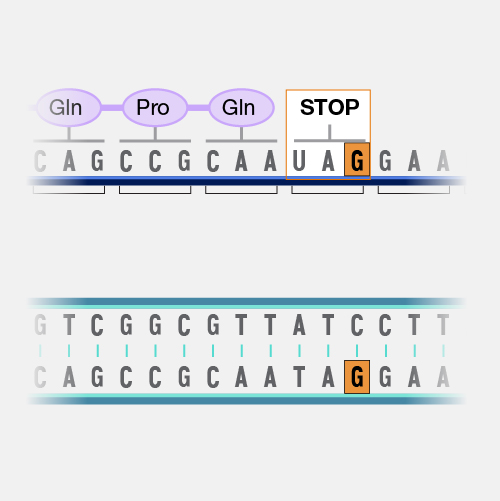
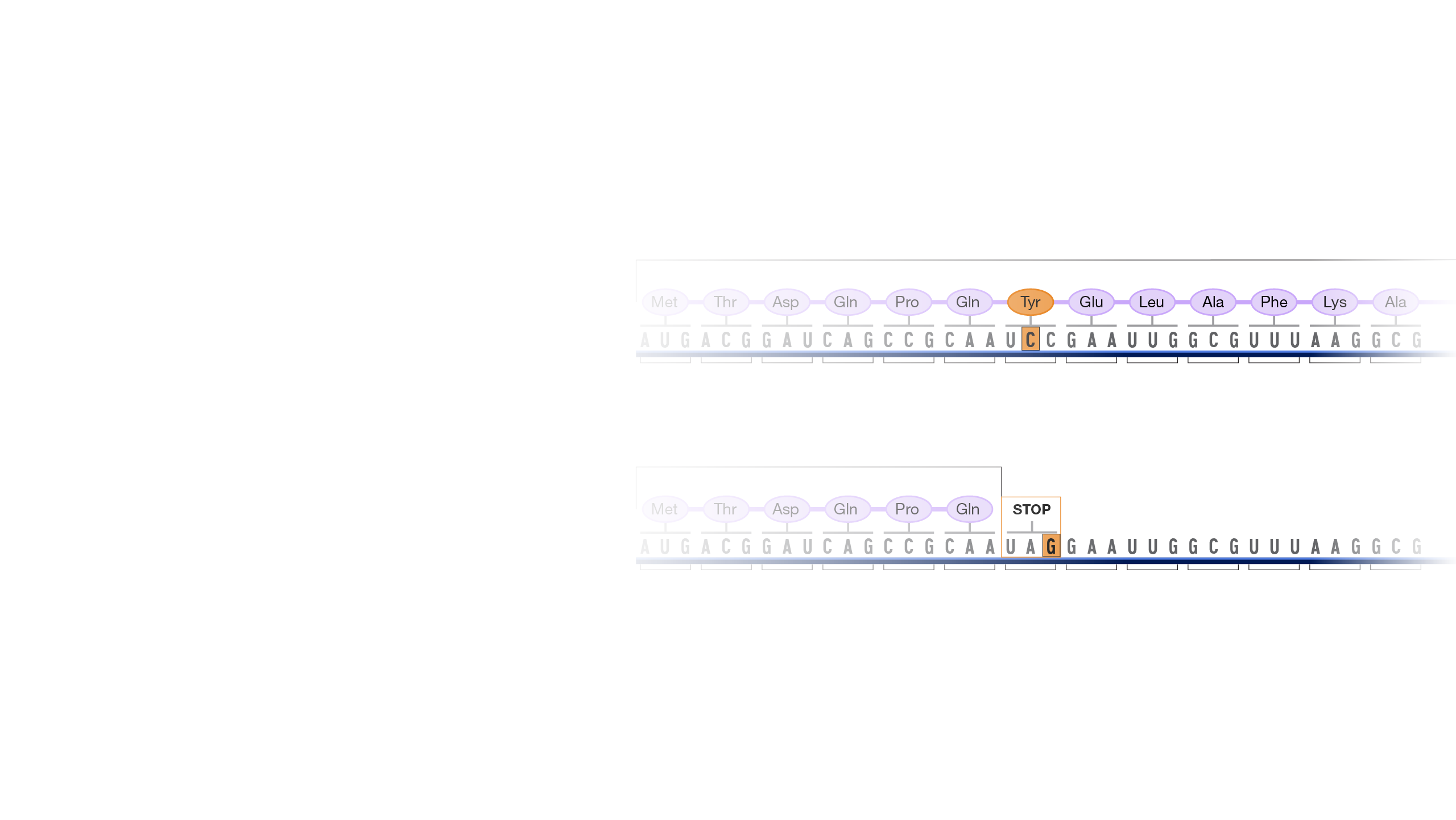
A point mutation occurs in a genome when a single base pair is added, deleted or changed. While most point mutations are benign, they can also have various functional consequences, including changes in gene expression or alterations in encoded proteins.

Narration
Point mutation. Did you know that on any average day, the 37 trillion cells in your body will acquire trillions of point mutations? These changes come from random errors in copying DNA as the cell divides or from environmental exposures, like cigarette smoke or even sunshine. It sounds a little scary, but almost all of these changes are in parts of your genome where it does not really matter. Your cells have also evolved ways to deal with some point mutations and correct them back to your original genome. But the very rare point mutation in your somatic cells, which are the cells that won't be sperm or eggs ultimately could lead to symptomatic disease.