X-Linked
Definition
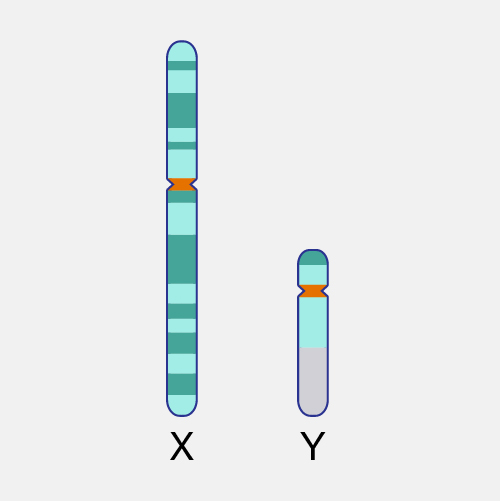
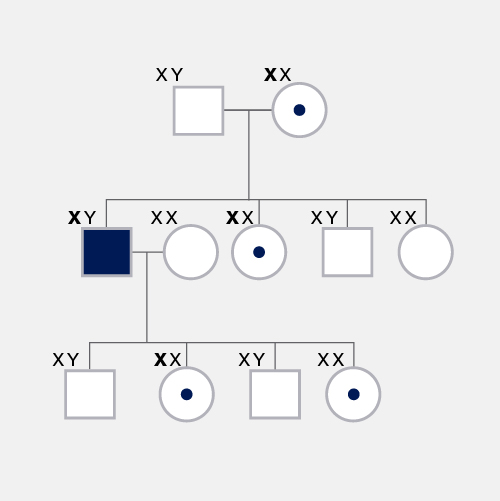
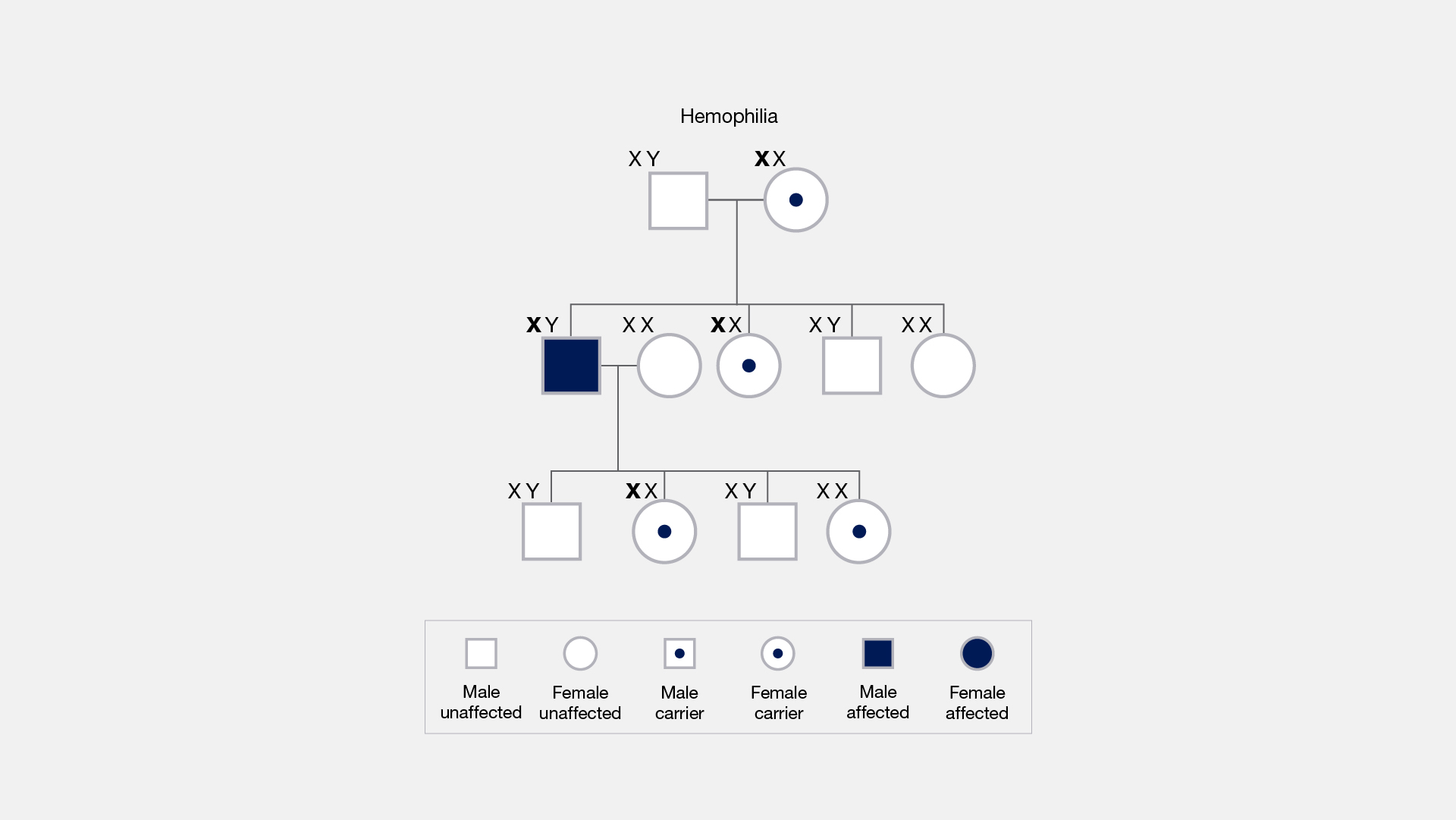
X-linked, as related to genetics, refers to characteristics or traits that are influenced by genes on the X chromosome. Humans and most other mammals have two sex chromosomes, X and Y. Females have two X chromosomes in their cells, while males have one X and one Y. In the case of an X-linked disease, it is usually males that are affected because they have a single copy of the X chromosome that carries the disease-causing mutation. In females, the presence of a second, non-mutated copy may cause different, milder, or no symptoms of a sex-linked disorder.
Narration
X-Linked. The way X-linked traits may manifest differently in females and males can be due to more complex phenomena such as X-inactivation, and exactly how copies of the X chromosome a person has. A simple rule of thumb for most X-linked conditions is that females generally have a milder version of the condition compared to males.