Nucleic Acids
Definition
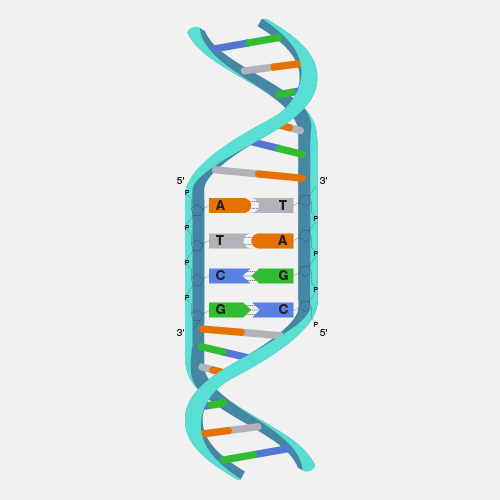
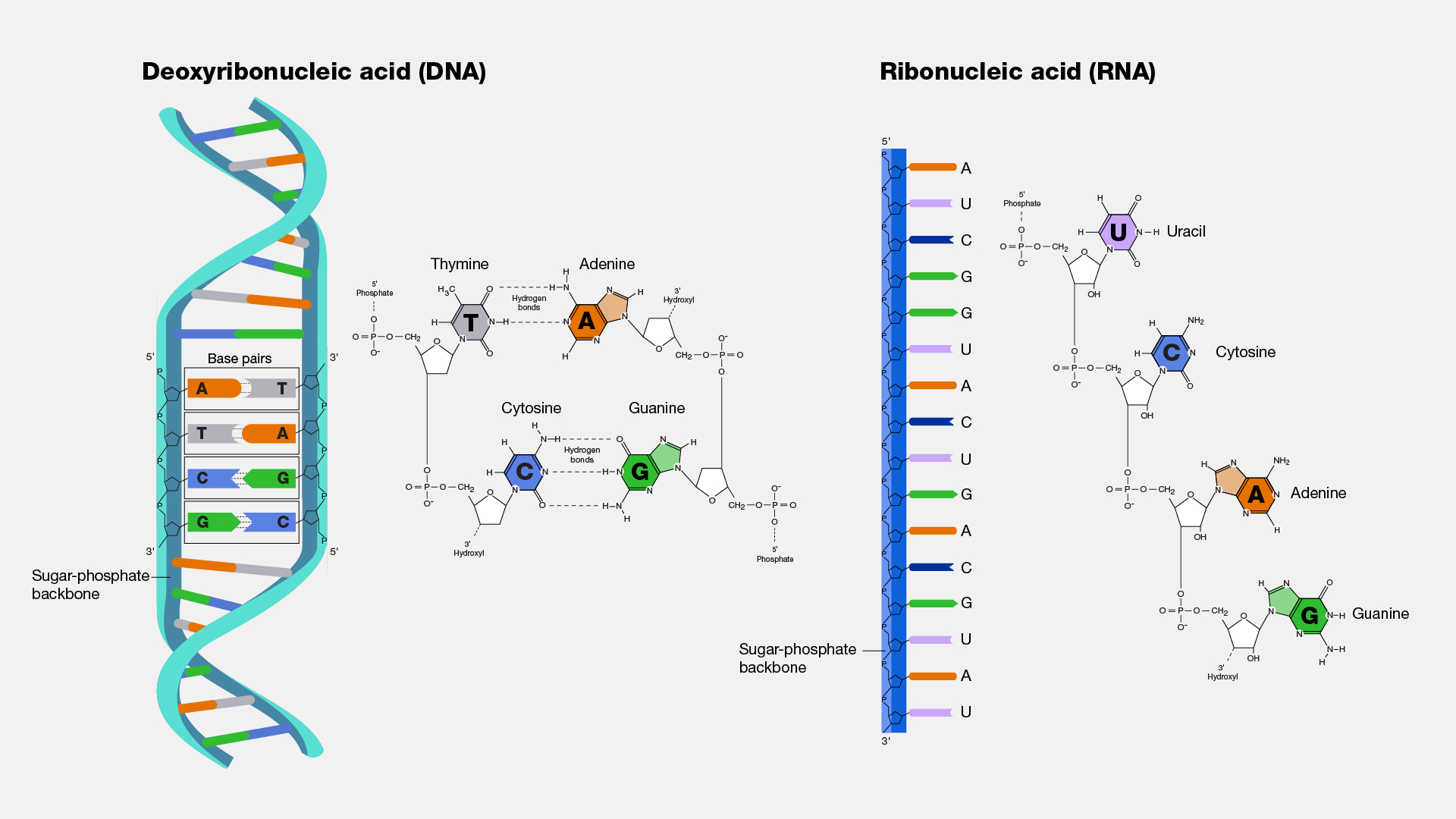
Nucleic acids are large biomolecules that play essential roles in all cells and viruses. A major function of nucleic acids involves the storage and expression of genomic information. Deoxyribonucleic acid, or DNA, encodes the information cells need to make proteins. A related type of nucleic acid, called ribonucleic acid (RNA), comes in different molecular forms that play multiple cellular roles, including protein synthesis.
Narration
Believe it or not, there are many songs devoted to nucleic acids. Something about them inspires art. I won’t sing any of them, but I did first learn about nucleic acids through a song in chemistry class. Nucleic acids are made of nitrogen-containing bases, phosphate groups, and sugar molecules. Each type of nucleic acid has a distinctive structure and plays a different role in our cells. Researchers who first explored molecules inside the nucleus of cells found a peculiar compound that was not a protein or a lipid or a carbohydrate. It was new. The discovery of this molecule — nuclein, which upon further understanding became nucleic acid — set in motion the eventual discovery of DNA.