Tandem Repeat
Definition
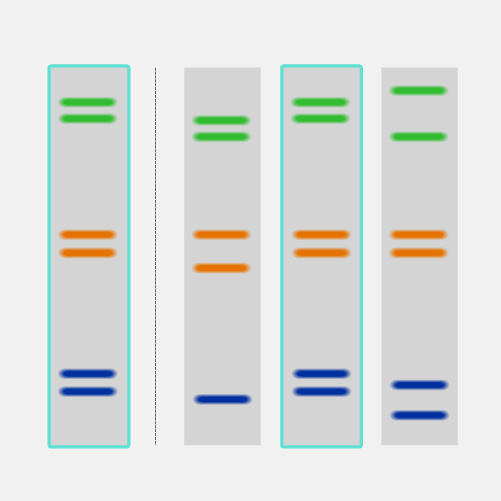
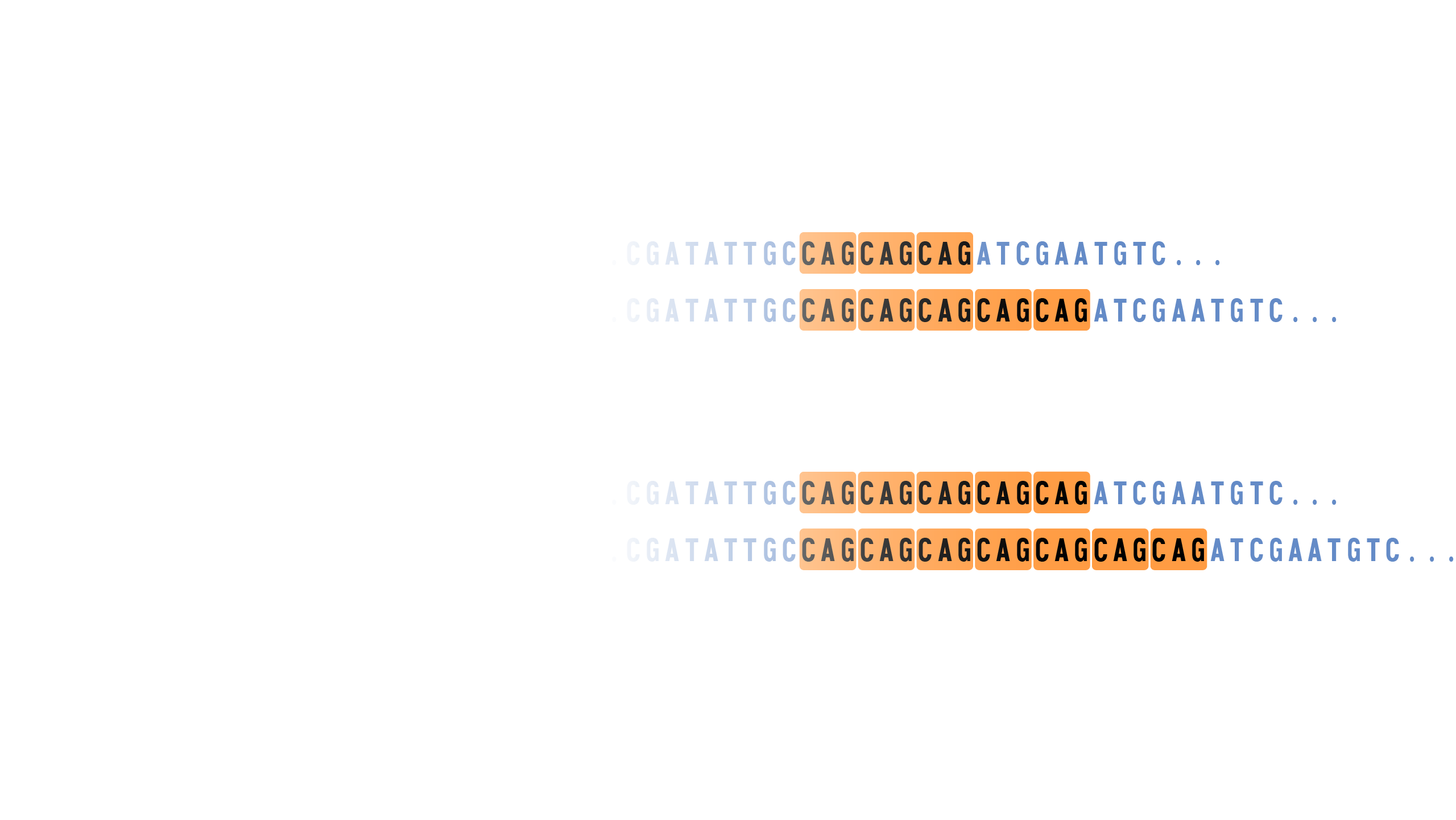
A tandem repeat is a sequence of two or more DNA bases that is repeated numerous times in a head-to-tail manner on a chromosome. Tandem repeats are generally present in non-coding DNA. In some cases, tandem repeats can serve as genetic markers to track inheritance in families. They can also be useful for DNA fingerprinting in forensic studies.

Narration
Tandem Repeats. Tandem repeats are interesting because they're recognizable repeats in the genome. They vary in the sequence that is repeated and how many times they are repeated in a given genome. One reason that makes them fascinating to study is that, depending on where they are in the genome, they can cause something as serious as Huntington's disease — which is a rare disease that causes the nerve cells in the brain to break down. They are also useful independent of health and disease status of a person, such as when they are used in forensic profiling to identify missing persons.

Lead Extramural Training Program Director
Training, Diversity and Health Equity Office