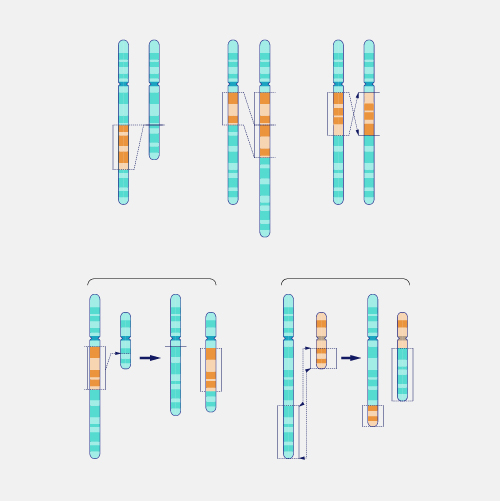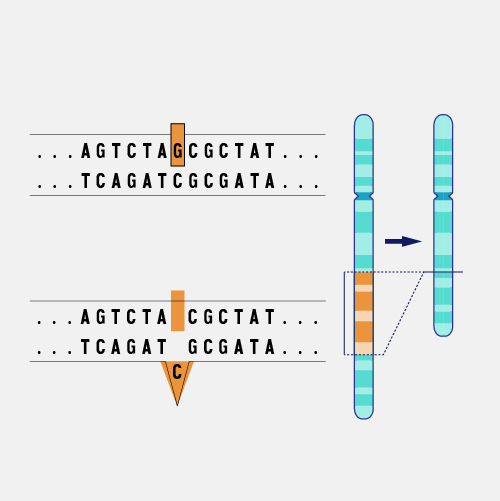
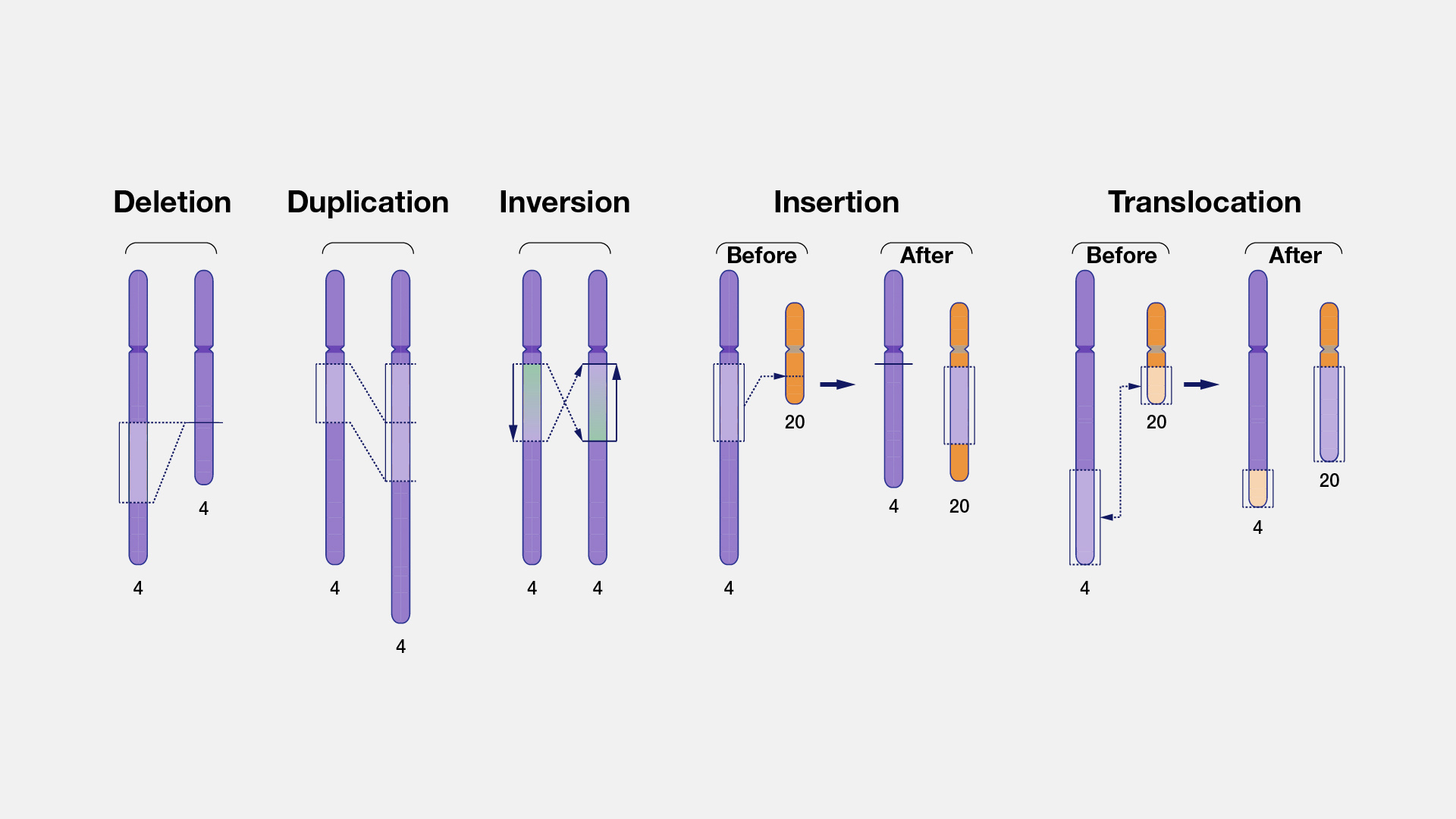
Structural Variation
Definition
Structural variation refers to differences between genomes involving larger segments of DNA. Genomic variants that involve differences of at least 50 nucleotides (bases) and as many as tens of thousands of nucleotides are considered structural variants. Structural variants can include nucleotides that have been inserted, deleted, inverted, or translocated (moved from one part of the genome to another).
Narration
When we consider genetic differences among people we usually think about single changes (individual nucleotides or basepairs) to the sequence of DNA. But bigger, structural changes in large chunks of DNA can also happen. Most of the genetic differences between any two people are single nucleotide changes numbering in the millions. A larger portion, however, of the total difference in DNA real estate between individuals is due to structural variants because they can be so large even though they only number in the thousands. If you think about the human genome like a book with 46 chapters, single nucleotide changes are many individual letter differences scattered between copies of the book. In contrast, structural variants can be differences in fragments of words, sentences, or even whole sets of paragraphs that can be copied, deleted, or shuffled around between pages or chapters. This means that structural variants, although less common, can nevertheless have a large impact on the function of genomes.