Hybridization
Definition
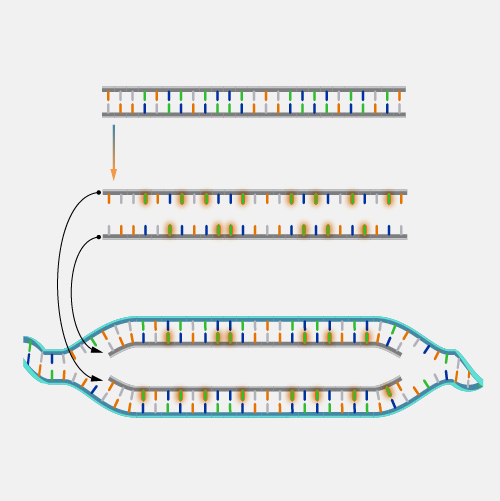
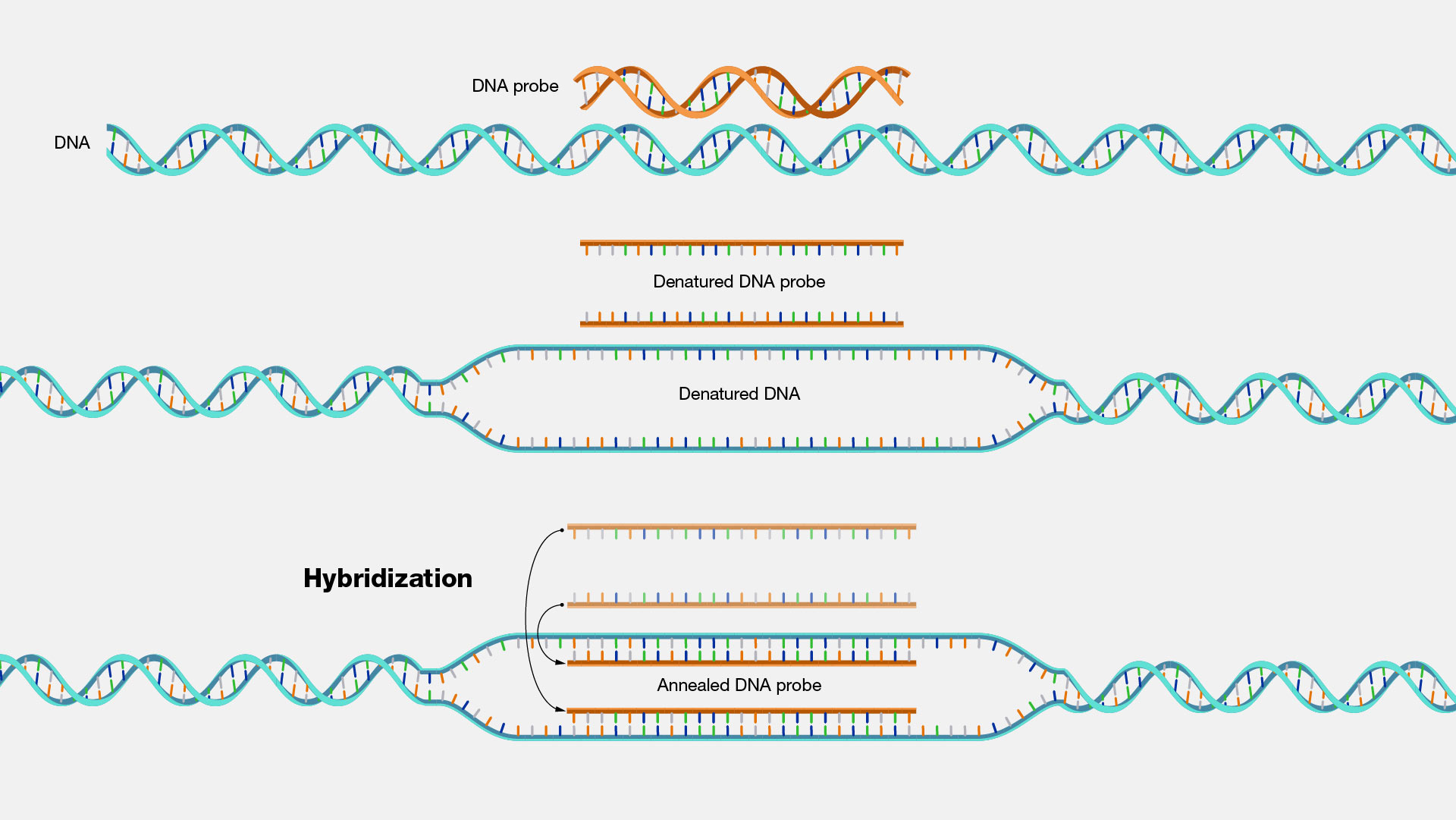
Hybridization, as related to genomics, is the process in which two complementary single-stranded DNA and/or RNA molecules bond together to form a double-stranded molecule. The bonding is dependent on the appropriate base-pairing across the two single-stranded molecules. Hybridization is an important process in various research and clinical laboratory techniques.
Narration
Hybridization. DNA is usually found as a double-stranded molecule. The two strands bind to one another in a complementary fashion by a process called hybridization. Naturally, when DNA is replicated, the new strand hybridizes to the old strand. In the laboratory, we can make small pieces of DNA, designed to screen for the presence or absence of certain DNA or RNA molecules in the cell. It also plays an important role in a procedure called polymerase chain reaction, known as PCR, where we amplify specific regions of the gene, and this is used in clinical testing.